Goals
- Understand the difference between the local and remote repository
- Understand branches
- Move a commit from the working directory to the remote repository
- Merge and update branches
Lesson
Understand the difference between the local and remote repository

- Let’s say we have a repo called learning_git and a branch called hotfix/add_docstring
- Look on bitbucket at the Branches and see how there is a branch called
hotfix/add_docstring - In a terminal in the
learning_gitrepo type:
git branch
- Why do you only see the
masterbranch?1 - Let’s get the branch
git fetch origin hotfix/add_docstring
- Now you not only have the
masterbranch but you also have the branch calledhotfix/add_docstringin your local repository. - Why do you have to include
originin the command?2
Understand branches
- A branch is an independent line of development
- Look at the utility module (
utility.py) - In a terminal in the
learning_gitrepo type:
git checkout hotfix/add_docstring
- The local utility module changed and now reflects the contents of the branch
hotfix/add_docstring - Switch back and forth between the
masterandhotfix/add_docstringbranch to understand what is happening. - Let me demonstrate how to modify the branch
- Make a change. Where does the change exist?3
- Stage the change –
git add modules/utility/utility.py - Commit the changes to the local repository
git commit -m 'making change'- Is the change in origin/remote repo?4
- Push the change –
git push origin hotfix/add_docstring
Exercise 1
- Go back to the
masterbranch - Create your own branch called {first name}_{last name}_branch (e.g.
git branch stephanie_sherman_branch) - Switch to your branch
- Add the function below to your branch in the
utility.pymodule- Place this code two lines below the
say_hello()function
- Place this code two lines below the
def say_goodbye(name):
goodbye_string = f'Goodbye {name}'
return goodbye_string
- Commit this function to the remote repo
- Go to bitbucket and see your change
Check Understanding
- You should now be able to:
- create a branch
- make a change
- move that change from your working folder to the remote repository
Merge and update branches
- Let’s say one of your teammates completed code review on the
hotfix/add_docstringbranch and it is ready to be incorporated into themasterbranch (I will merge it now). - Now, there are changes in
masterthat are not included in your branch. - Let’s get our branch up-to-date with the
masterbranch by mergingmasterinto our branch
git merge master
- Why does git say it is already up to date?5
- Go to the Branches page and examine the “Ahead Behind” graphic of your branch
- Let’s switch to the master branch and get the changes
git checkout master
git pull origin master
- Open the
utility.pymodule and verify that you have the updated changes - Now that you have the updated changes it is time to add them to your branch
git checkout {first name}_{last name}_branch
git merge master
- Open the
utility.pymodule and verify that you have the updated changes in the branch - If I go to bitbucket would I see the changes in my branch?6
git push origin {first name}_{last name}_branch
- Now check bitbucket
Exercise 2
- Get a teammate’s branch
- Switch to that branch
- Go to bitbucket and create a pull request on your branch and assign a reviewer.
Check Understanding
- You should now be able to:
- Update any branch from remote
- Fetch any branch from remote
- Understand the beginning graphic
Bonus Material
Merge conflicts
- Sometimes the automated git merging strategies fail and require manual merging
- In bitbucket merge conflicts can be seen in pull requests diff
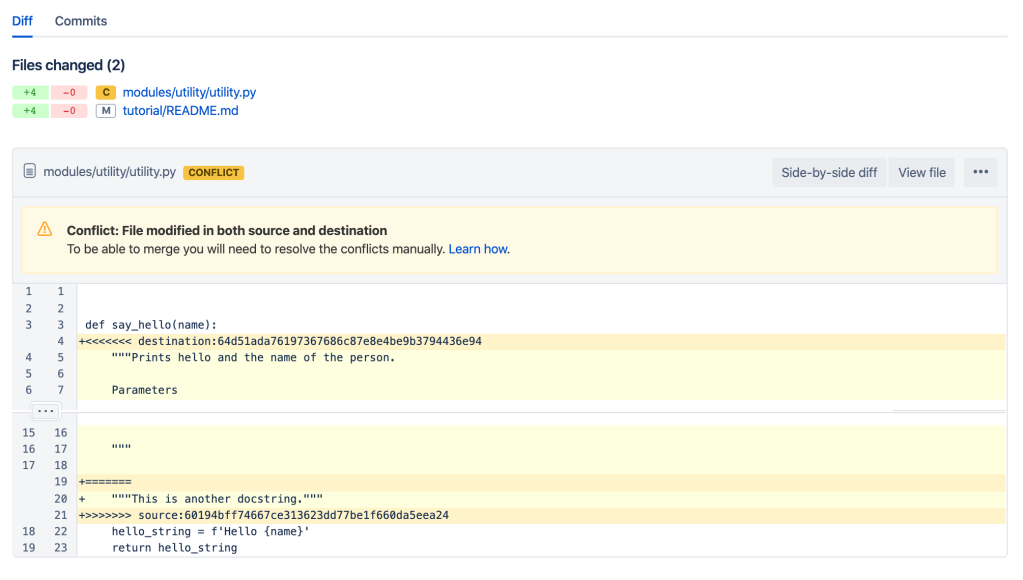
- Handling merge conflicts in your development branch may be the best approach
- Atom has a nice interface to manually resolve merge conflicts
- If you would like to use atom as your default editor open your
.bash_profilein your home directory and add:
export EDITOR='atom'
- Open a new terminal (or source your
.bash_profile) - Merge master into the
enhancement/if_timebranch7 - Open atom and use the sidebar to examine the conflicts and navigate to them
- Click Use me to indicate which version of the code you would like to keep
- If you do not want to use either, right click on the dots next to Use me and click Dismiss. Be sure to delete the git syntax
>>>>>>,<<<<<<<,======= - After you resolve the conflict, stage your changes, commit, then push
- Now your branch should be ready to merge to master
example of the atom interface
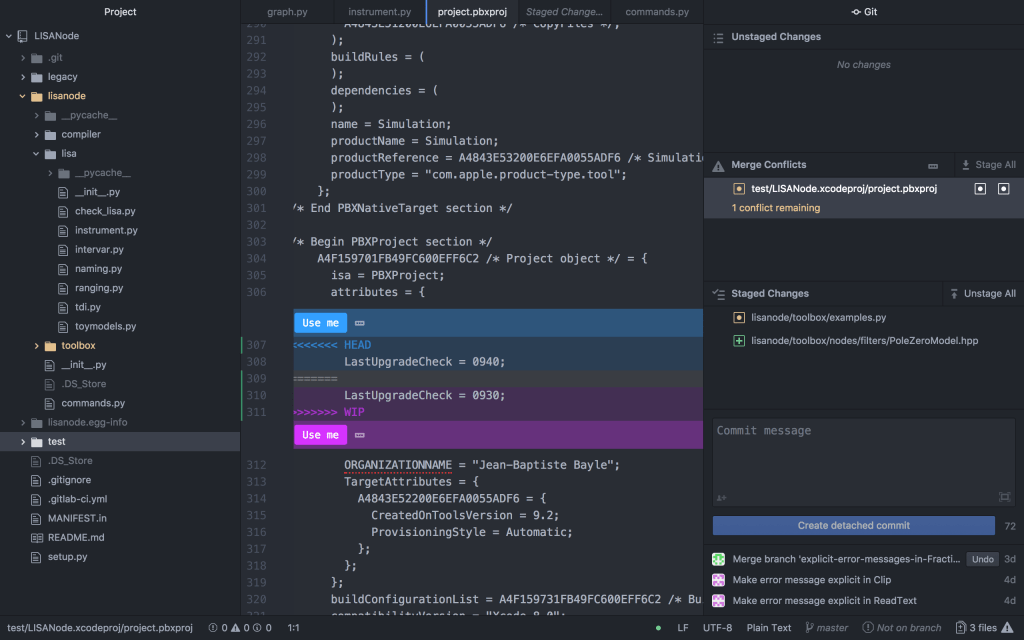
Conflict Dividers
<<<<<<< HEAD=======>>>>>>> <branch_to_merge>- “The
=======line is the “center” of the conflict. All the content between the center and the<<<<<<< HEADline is content that exists in the current branch master which the HEAD ref is pointing to. Alternatively all content between the center and>>>>>>>new_branch_to_merge_later is content that is present in our merging branch”
Helpful commands
git status: Show the files that are staged, unstaged, and untrackedgit diff: Show unstaged changes in your working directory that are not yet in your local repo- You can always quit
git diffby typeqthen return
- You can always quit
Clean up
- In order to walk through this tutorial again we need to revert back to the commit right before we started the lesson.
Answers
1: The hotfix/add_docstring is not located in your local repo until you fetch it from remote.
2: origin is shorthand for remote repository that a project was originally cloned (https://www.git-tower.com/learn/git/glossary/origin). In order to pull from remote you have specify it.
3: In the working directory
4: No, the change has not yet been pushed to remote, it only exists in your local repo
5: Our local repository does not have the updated changes. The changes only exist in remote.
6: No, the changes are only local they have not been pushed to remote
7: git merge master


